Fats play an important role in our diets. Nutritionists recommend eating a diet low in fat, particularly low in saturated fat.
What’s the difference between saturated, polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats?
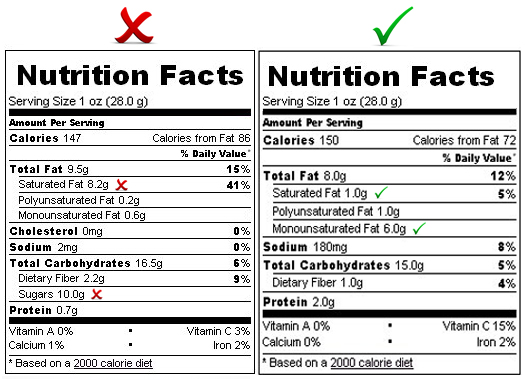
Saturated fats
Saturated fats tend to increase ‘bad’ cholesterol levels in the blood as well as total cholesterol levels. They are found mostly in animal products e.g. meat and full cream dairy products. Two non-animal exceptions are palm kernel and coconut oils which also contain saturated fat and are often found in commercial biscuits and cakes.
Monounsaturated fats
These fats can benefit the body by reducing the level of total and ‘bad’ cholesterol and increasing the level of ‘good’ cholesterol in the blood. Found in foods such as olives, peanuts, avocados and canola oil.
Polyunsaturated fats
These fats tend to lower the total and ‘bad’ cholesterol levels while maintaining the level of ‘good’ cholesterol. Found in margarines, nuts, soymilks, seeds and vegetable oils.
Omega-3
A type of polyunsaturated fat, which research suggests may help maintain healthy blood pressure and blood fat levels. Found in linseed, canola oil, soybeans, walnuts and dark green vegetables (e.g. spinach, green peas.)
All fats have the same number of kilojoules and need to be eaten in moderation – especially if you are trying to control your weight.
Leave A Comment